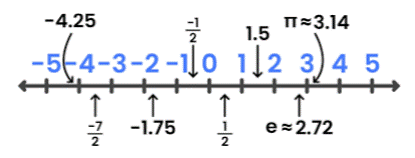Numbers play significant roles in everyday life — in business for buying and selling; for measuring of a patient’s vitals (weight, temperature, rate of heartbeat etc.) in the hospital; for checking the speed limit of a moving vehicle when driving; to represent the quantities of food substances that should be combined to constitute a balanced diet to ensure good nutrition, etc.
As a class or in small groups discuss the following scenarios:
1. Imagine a world without numbers. What challenges would this create? Do we consider numbers essential?
2. How do we use numbers in our everyday lives? How did you use them in coming to school? Have you already used them in your lessons?
3. How do different professions use them? Can you think of a profession where numbers are not required?
4. Looking back to junior high, can we remember different types of numbers that we came across? E.g., odd numbers, even numbers, what other types? Below is a breakdown of some of the different types of numbers.
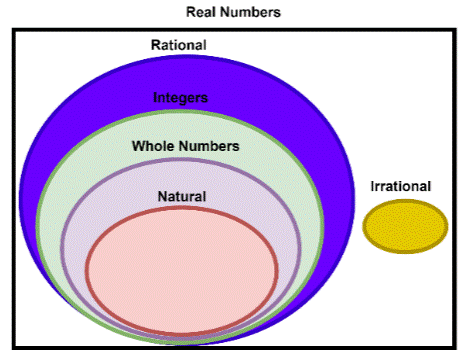
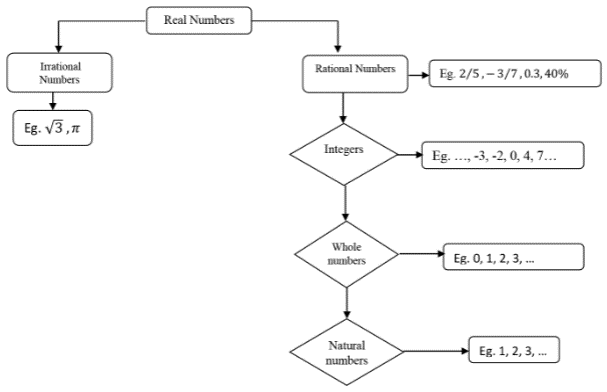
Key Concepts in the Real Number System
• Natural Numbers: These are counting numbers that contain positive numbers from 1 to infinity. The set of natural numbers is denoted as N, where N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, ...}
• Whole Numbers: These numbers start from 0 to infinity. Set of whole numbers is denoted as W, where W = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, ...}.
• Integers: These contain infinite positive and negative whole numbers. A set of integers is usually denoted as Z, where Z = {..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ...}
• Irrational Numbers: These numbers cannot be expressed in the form a/b, where a and b are integers but b≠0. The set of irrational numbers is usually denoted as Q'. Examples of irrational numbers are √2, √3, 2√2, 2√5, √8, π . These numbers are non-terminating and non-recurring decimals.
• Real Numbers: These are the combination of rational numbers and irrational numbers.
• Terminating Decimals: They are decimal numbers that end (i.e. Terminate) after a finite number of digits.
• Non-terminating Decimals: They are decimal numbers that continues endlessly with or without repeating digits. These are numbers that do not end or terminate.
• Recurring Decimals: They are decimal representations of rational numbers where one or more digits repeat infinitely. For example, 0.33 , 5.25252525... , 0.1535
• Closure Property: A set is said to be closed under an operation if performing that operation on any two elements from the set always produces a result that is also in the set.
Which of the sets above contains the most elements and which the fewest? Can you explain why this is the case?